
Note that Red Hat resigned leadership of OpenJDK 6 at the beginning of 2017 and this was then taken up by Azul Systems.
The OpenJDK 6 project, which is based on JDK 7, retrofitted to provide an open-source version of Java 6. The OpenJDK 7u project, which is based on JDK 7 and produces updates to the existing Java 7 releases. The OpenJDK 8 project, which is the basis for JDK 8, was released on 18 March 2014. The OpenJDK 8u project, which is based on JDK 8 and produces updates to the existing Java 8 releases. The OpenJDK 9 project, which is the basis for JDK 9. There are several separate OpenJDK & JDK Project development branches: Unlike past JDK Release Projects, which produced just one feature release and then terminated, this long-running project will produce all future JDK feature releases and will ship a feature release every six months according to a strict, time-based model. Since JDK 10, the effort to produce an open-source reference implementation of the Java SE Platform was moved over to the JDK Project. OpenJDK was initially based only on the JDK 7 version of the Java platform. The experimental -XX:+EnableJVMCIProduct flag enables the use of Graal JIT (JEP 317). 
OpenJDK 9+ supports AOT compilation ( jaotc) using GraalVM (JEP 295).
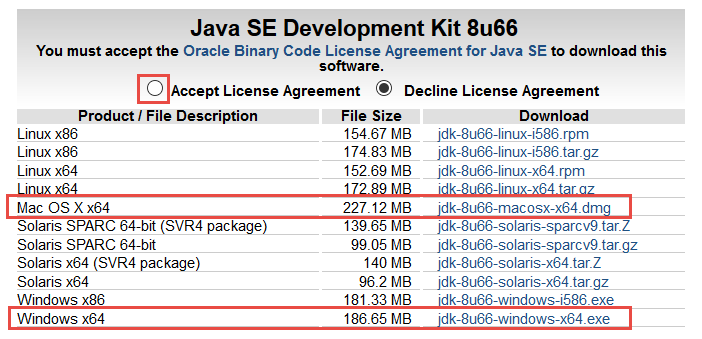
The only currently available free plugin and Web Start implementations as of 2016 are those provided by IcedTea. Sun previously indicated that they would try to open-source these components, but neither Sun nor Oracle have done so. The web-browser plugin and Web Start, which form part of Oracle Java, are not included in OpenJDK. The OpenJDK project produces a number of components: most importantly the virtual machine ( HotSpot), the Java Class Library and the Java compiler ( javac). 5.4 Collaboration with IBM, Apple, and SAP.
#Java mac os x 64 software#
4 IcedTea and inclusion in software distributions.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
